Final Project - SDU Robotics Summer Course
Implementation of two motion planning algorithms:
- Rapidly-exploring Random Tree (RRT)
- Potential Field
The project report can be found here
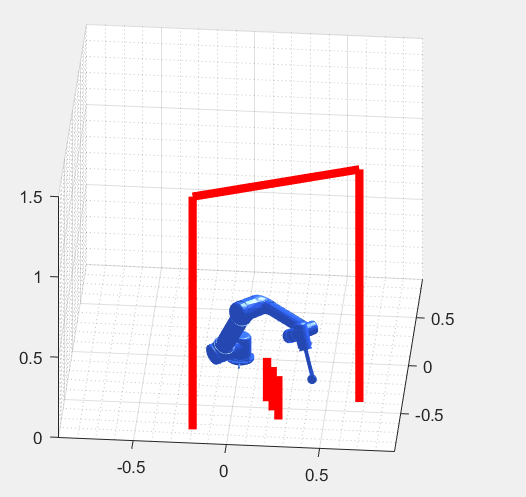
Both algorithms find collision-free paths for the UR5 robotic arm (Universal Robots site) to perform pick-and-place tasks.
Scripts MPExtendRRT.m and PotentialField.m display a simulation of the UR5 robot following the path found and the obstacles defined.
A *.script output file is generated with the commands for the real UR5 robot. Example:
...
movej([-0.83856, -1.96147, -1.06408, -1.06838, 1.58115, -1.01197], a=1, v=1, t=0, r=0)
movej([-0.834858, -2.04677, -1.06577, -1.07883, 1.61465, -0.997554], a=1, v=1, t=0, r=0)
movej([-0.860245, -2.12685, -1.0378, -1.09263, 1.64701, -0.967192], a=1, v=1, t=0, r=0)
movej([-0.83583, -2.1846, -1.08443, -1.11736, 1.62908, -1.02161], a=1, v=1, t=0, r=0)
...
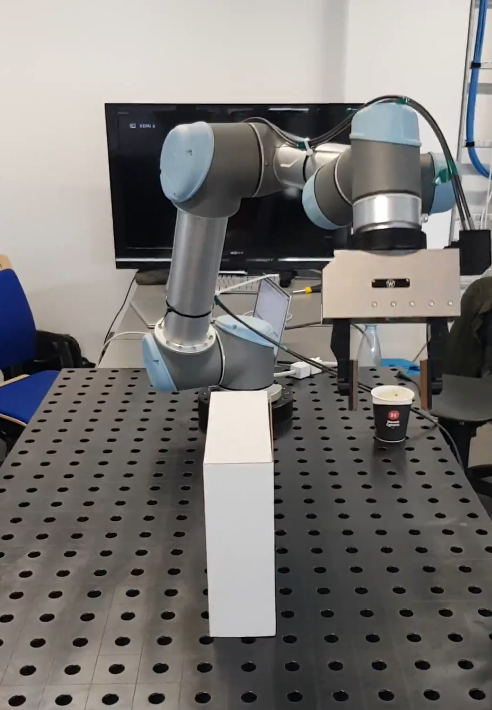
Video of the real UR5 robot following the generated path using the RRT algorithm
Usage
Set up a a MEX compiler:
mex -setup C++
Initialize toolbox parameters:
run_me
Load demo variables (optional):
load demo_vars.mat
Run motion planning algorithm:
MPExtendRRT(initial_configuration, goal_configuration, obstacles)
PotentialField(initial_configuration, goal_configuration, obstacles)
initial_configuration is the initial configuration of UR5 (dimension: 1*6, unit: radian)
goal_configuration is the goal configuration of UR5 (dimension: 1*6, unit: radian)
obstacles represents all the capsule obstacles in the workspace (dimension: n*7)
format of each row of obstacles: [P_ini, P_end, r] where P_ini is the x-, y- and z- coordinates of the initial point of the interal line segment of the capsule (diemsion: 1*3 unit: meter), P_end is the x-, y- and z- coordinates of the end point of the interal line segment of the capsule (diemsion: 1*3 unit: meter), r is the radius of the capsule (scalar, unit: meter)